
Light Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1911
- Caliber : 75 mm
- Shell Weight : 12.7 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 70 m/sec
- Weight : 49.8 kg
- Range : 130-420 m
It is an obsolete infantry mortar used in WWI. It has no type designation.

Type 11 70mm Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1922
- Caliber : 70 mm
- Barrel Length : 0.75 m (L10.7)
- EL Angle of Fire : +43 to +73 Degrees
- Shell Weight : 2.5 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 147 m/sec
- Weight : 63 kg
- Range : 1,550 m
- Production Qty : 234
Type 11 had a rifled bore and a trigger to fire like old type mortars in WWI. Later, Type 11 had been replaced with Type 92 Infantry Gun.
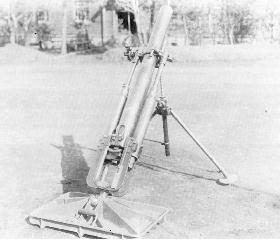
Type 94 90mm Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1935
- Caliber : 90.5 mm
- Barrel Length : 1.27 m
- EL Angle of Fire : +45 to +80 Degrees
- Shell Weight : 20 or 40 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 227 m/sec
- Weight : 159 kg
- Range : 3,800 m
- Production Qty : 450
From Type 94, Japanese mortars had a smooth bore and could be fired by dropping a shell. Type 94 was used in the Chinese-Japanese War, but Type 94 was rated low, because it was too heavy for infantry to carry.
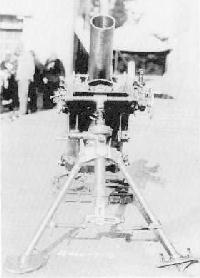
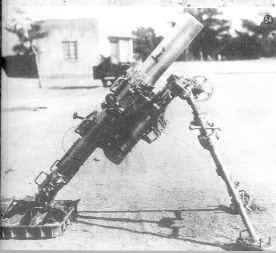
Type 96 150mm Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1936
- Caliber : 150.5 mm
- Barrel Length : 1.325 m
- EL Angle of Fire : +45 to +80 Degrees
- Shell Weight : 25.65 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 214 m/sec
- Weight : 722 kg
- Range : 3,900 m
- Production Qty : 90
Type 96 was the largest infantry mortar in IJA. It is said that Type 96 was used in China and Iwo Jima, but its details are unkown.

Type 97 81mm Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1937
- Caliber : 81.4 mm
- Barrel Length : 1.269 m (L15.6)
- EL Angle of Fire : +45 to +85 Degrees
- Shell Weight : 3.33 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 196 m/sec
- Weight : 67 kg
- Range : 2,850 m
Type 97 is a most popular mortar in IJA and it was widely used during WWII. This mortar was also produced by IJN under the IJN name of Type 3 Mortar.

Type 97 90mm Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1937
- Caliber : 90.5 mm
- Barrel Length : 1.217 m
- EL Angle of Fire : +45 to +85 Degrees
- Shell Weight : 5.26 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 227 m/sec
- Weight : 172.5 kg
- Range : 3,800 m
- Production Qty : 600
Type 97 is a simplified model of Type 94 by removing the recoil mechanism.
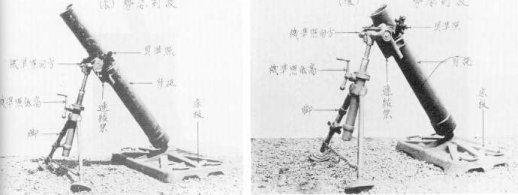
Type 97 150mm Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1941
- Caliber : 150.5 mm
- Barrel Length : 1.935 m (Long Barrel), 1.395 m (Short Barrel)
- EL Angle of Fire : +45 to +80 Degrees
- Shell Weight : 23.8 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 212 m/sec
- Weight : 342 kg (Long Barrel), 232.5 kg (Short Barrel)
- Range : 3,850 m
- Production Qty : 110
Type 97 is a simplified model of Type 96 by removing the recoil mechanism. There are two sub-models, the short barrelled model and the long barrelled model.

Type 99 81mm Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1939
- Caliber : 81 mm
- Barrel Length : 0.62 m
- EL Angle of Fire : +45 to +85 Degrees
- Shell Weight : 3.33 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 82 m/sec
- Weight : 24.8 kg
- Range : 650 m
Type 99 is an airborne model and it is able to be disassembled.

Type 2 120mm Infantry Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1942
- Caliber : 120 mm
- Barrel Length : 1.535 m
- EL Angle of Fire : +40 to +80 Degrees
- Shell Weight : 12.76 kg
- Muzzle Velocity : 239 m/sec
- Weight : 260 kg
- Range : 4,200 m
- Production Qty : 750
Type 2 was an effective mortar with long range and large caliber. However, its production had commenced in the late WWII, and its service in action was limited.
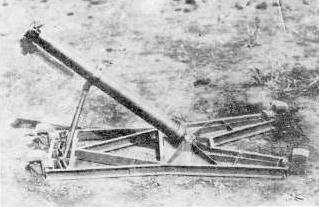
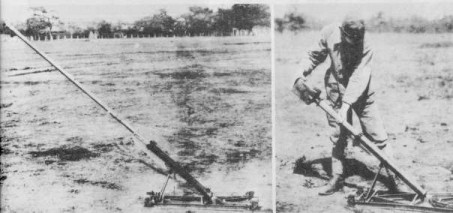
Type 98 50mm Mortar
- Introduced Year : 1938
- Caliber : 50 mm
- Barrel Length : 0.65 m
- EL Angle of Fire : Fixed 40 Degrees
- Muzzle Velocity : 147 m/sec
- Weight : 22.4 kg
Type 98 was used by engineers to detonate the barbed wire. It discharges the spigot bomb (right bottom) or the bangalore torpedo with fins (left bottom). The range of fire is between 300 and 420 m depending on its ammo.











